Intermittent Fasting And Alzheimer's Disease
Intermittent fasting and alzheimer's disease. Particularly the effect this might have on neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimers disease. Intermittent fasting and caloric restriction ameliorate age-related behavioral deficits in the triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimers disease. Intermittent fasting provides one method of decreasing insulin while also decreasing caloric intake.
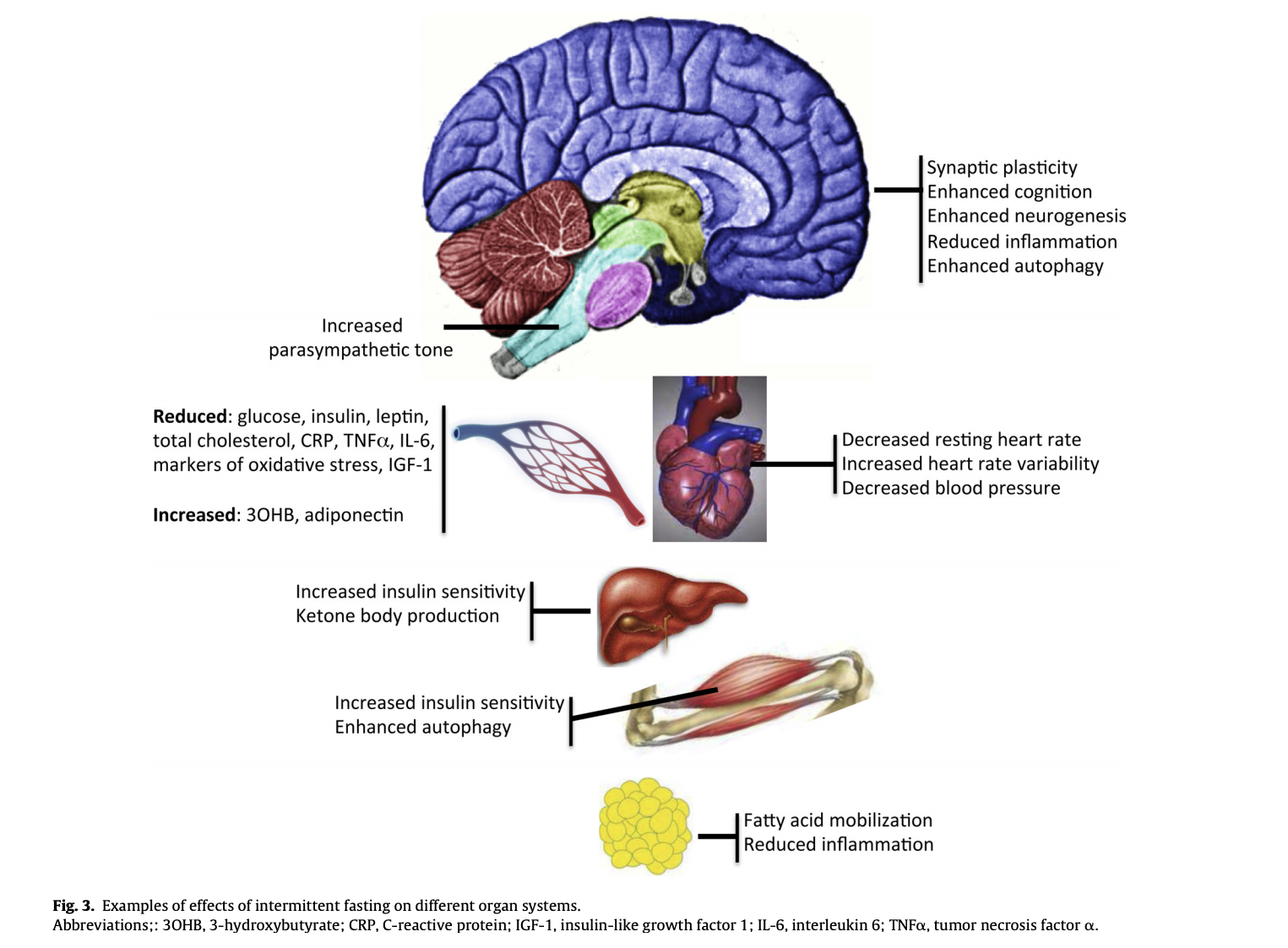
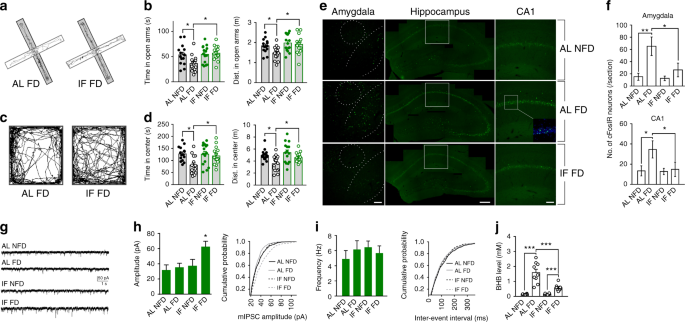
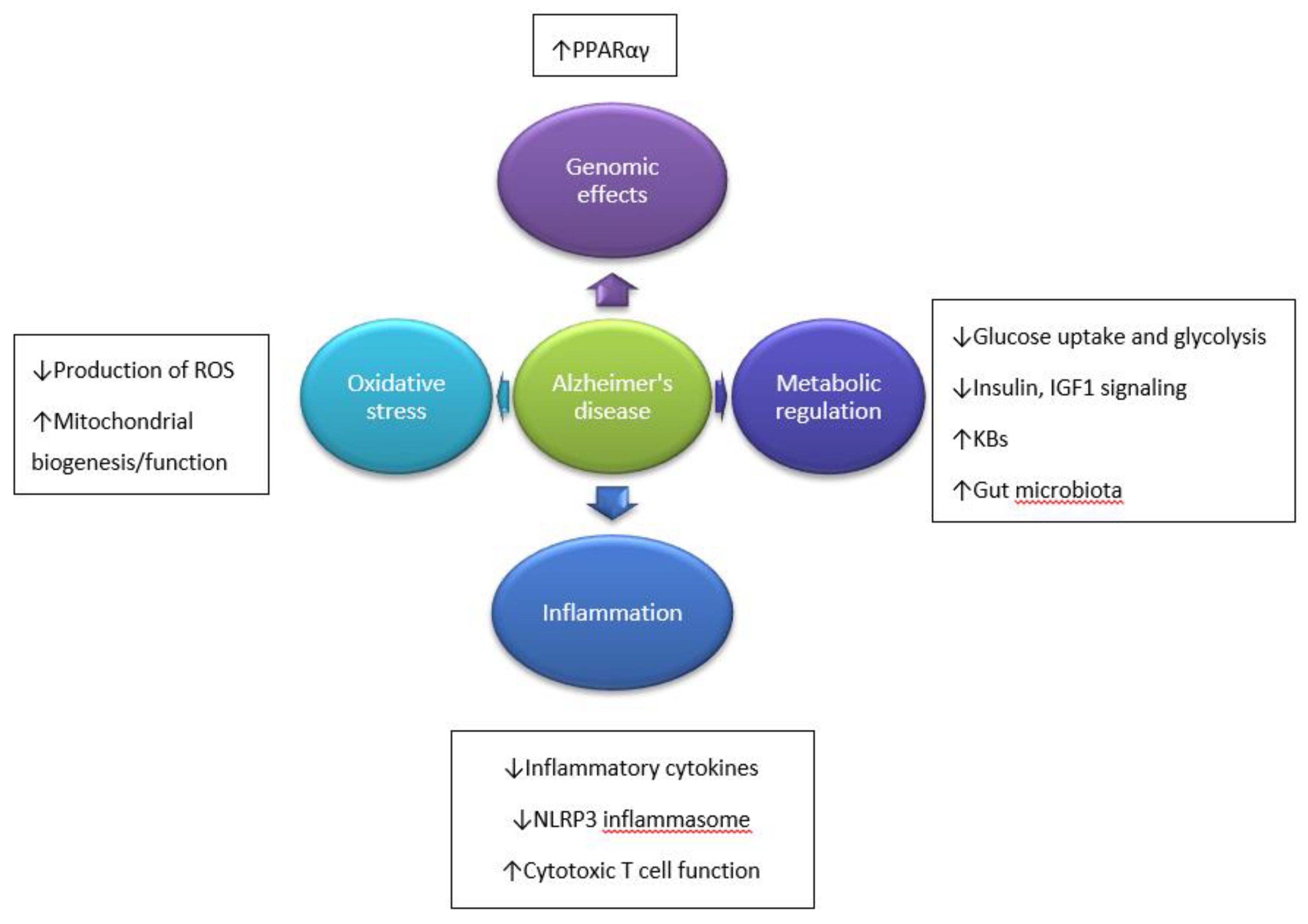
Emerging findings are revealing cellular and molecular mechanisms by which IF increases the resistance of cells tissues and organs to stress and common diseases associated with aging and sedentary overindulgent lifestyles. Alzheimers disease increased glucose oxidation whereas intermittent fasting elevated fat oxidation as a fuel source. Alzheimers disease and intermittent fasting deteriorated insulin resistance in the fasting state but intermittent fasting decreased serum glucose levels after oral glucose challenge by increasing insulin secretion.
We examined the evidence for intermittent fasting IF as a preventative tool to influence β-amyloid in animal models of Alzheimers disease AD. Intermittent Fasting and Its Effects on the Brain Alzheimers Disease Research Center Intermittent Fasting and Its Effects on the Brain Thursday October 8 2020 As intermittent fasting has risen in popularity over the last decade researchers have been exploring its. Researchers are now exploring opportunities to study intermittent fasting in humans.
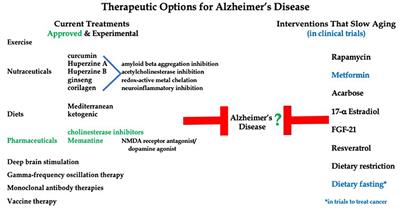
Fasting might prevent Alzheimers disease Alzheimers disease AD is characterized by the abnormal accumulation of proteins. Nevertheless the mechanisms for these benefits are poorly understood. Additionally the potential benefits of IF combined with other positive lifestyle factors such as exercise should also be further investigated.
Starving yourself once or twice a week could help protect the brain against degenerative diseases such as Alzheimers and Parkinsons claim a group scientists. Avoid snacking or eating at nighttime all the time. No studies have yet been published testing intermittent fasting in people with neurodegenerative diseases Mattson says.
Cardiovascular disease obesity Alzheimers disease and even certain types of cancers. A Scopus Ovid PubMed and Web of Science WoS search yielded 29 results using the keywords amyloid beta intermittent fasting. We examined the evidence for intermittent fasting IF as a preventative tool to influence -amyloid in animal models of Alzheimers disease AD.
There are myriad methods of IF circulating all of which split the day or. Intermittent fasting IF is not a conventional diet plan but an eating pattern that rotates between periods of fasting and eating and is repeated day after day.
The findings resonate with decades-old studies that show a link between caloric intake and oxidative rustingthe stress on cells that comes when people get older and take in food.
IF appears to be promising for its potential to protect the brain from the effects of aging and disease. Intermittent fasting provides one method of decreasing insulin while also decreasing caloric intake. Alzheimers disease AD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive decline in cognitive function associated with the neuropathological hallmarks amyloid beta-peptide Abeta plaques. But rates of obesity and diabetes are increasingly common and both are risk factors for dementia. Limit the hours of the day when you eat and for best effect make it earlier in the day between 7 am to 3 pm or even 10 am to 6 pm but definitely not in the evening before bed. IF appears to be promising for its potential to protect the brain from the effects of aging and disease. Ensure at least 12 hours between your last meal of the day and breakfast and make sure you finish your last meal of. New and exciting. Avoid snacking or eating at nighttime all the time.
The findings resonate with decades-old studies that show a link between caloric intake and oxidative rustingthe stress on cells that comes when people get older and take in food. Intermittent Fasting and Its Effects on the Brain Alzheimers Disease Research Center Intermittent Fasting and Its Effects on the Brain Thursday October 8 2020 As intermittent fasting has risen in popularity over the last decade researchers have been exploring its. Limit the hours of the day when you eat and for best effect make it earlier in the day between 7 am to 3 pm or even 10 am to 6 pm but definitely not in the evening before bed. Mattson also noted that in mice studies intermittent fasting dramatically improved heart health and prevented the symptoms of Alzheimers. Nevertheless the mechanisms for these benefits are poorly understood. A Scopus Ovid PubMed and Web of Science WoS search yielded 29 results using the keywords amyloid beta intermittent fasting. Alzheimers disease AD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive decline in cognitive function associated with the neuropathological hallmarks amyloid beta-peptide Abeta plaques.
































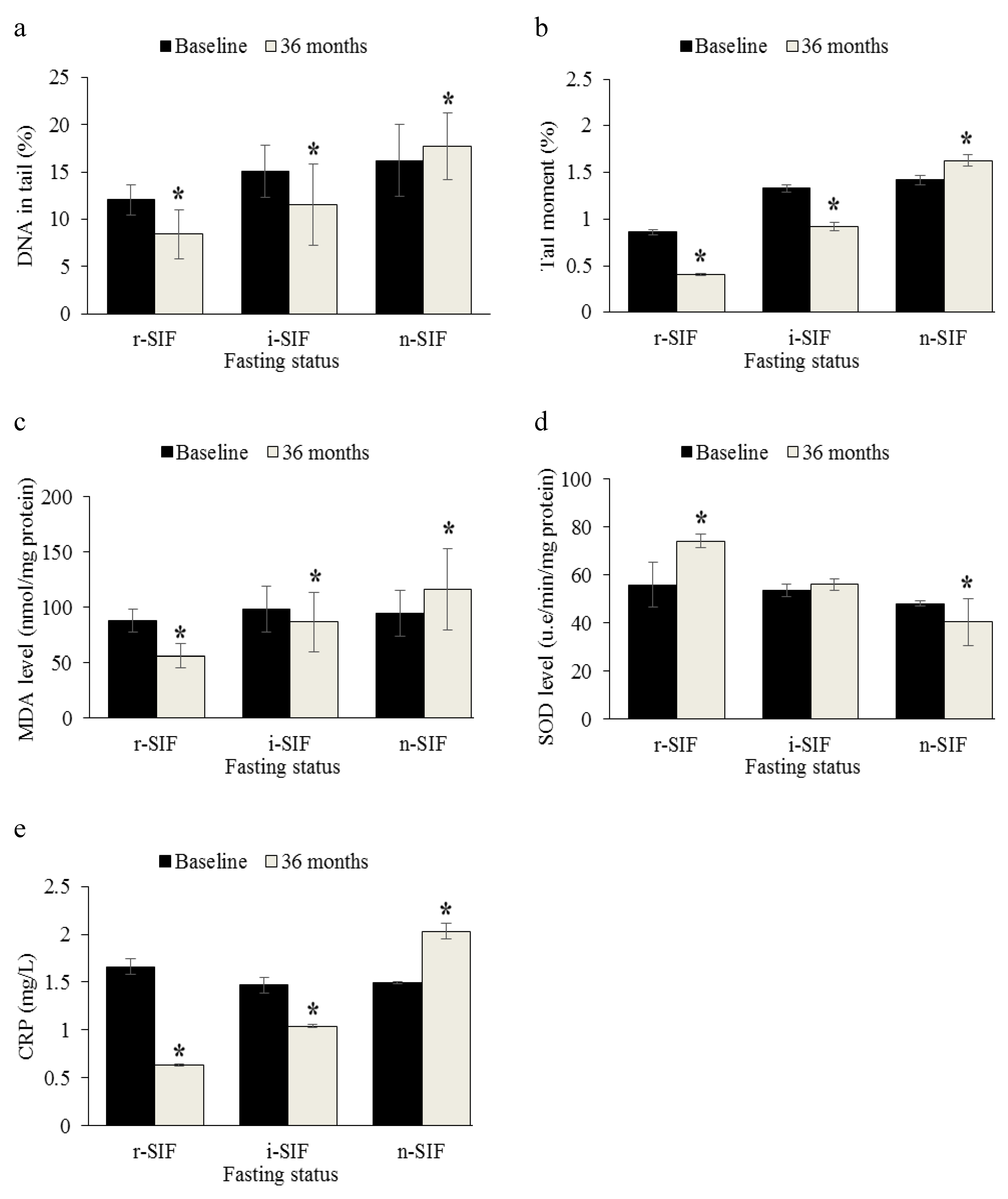


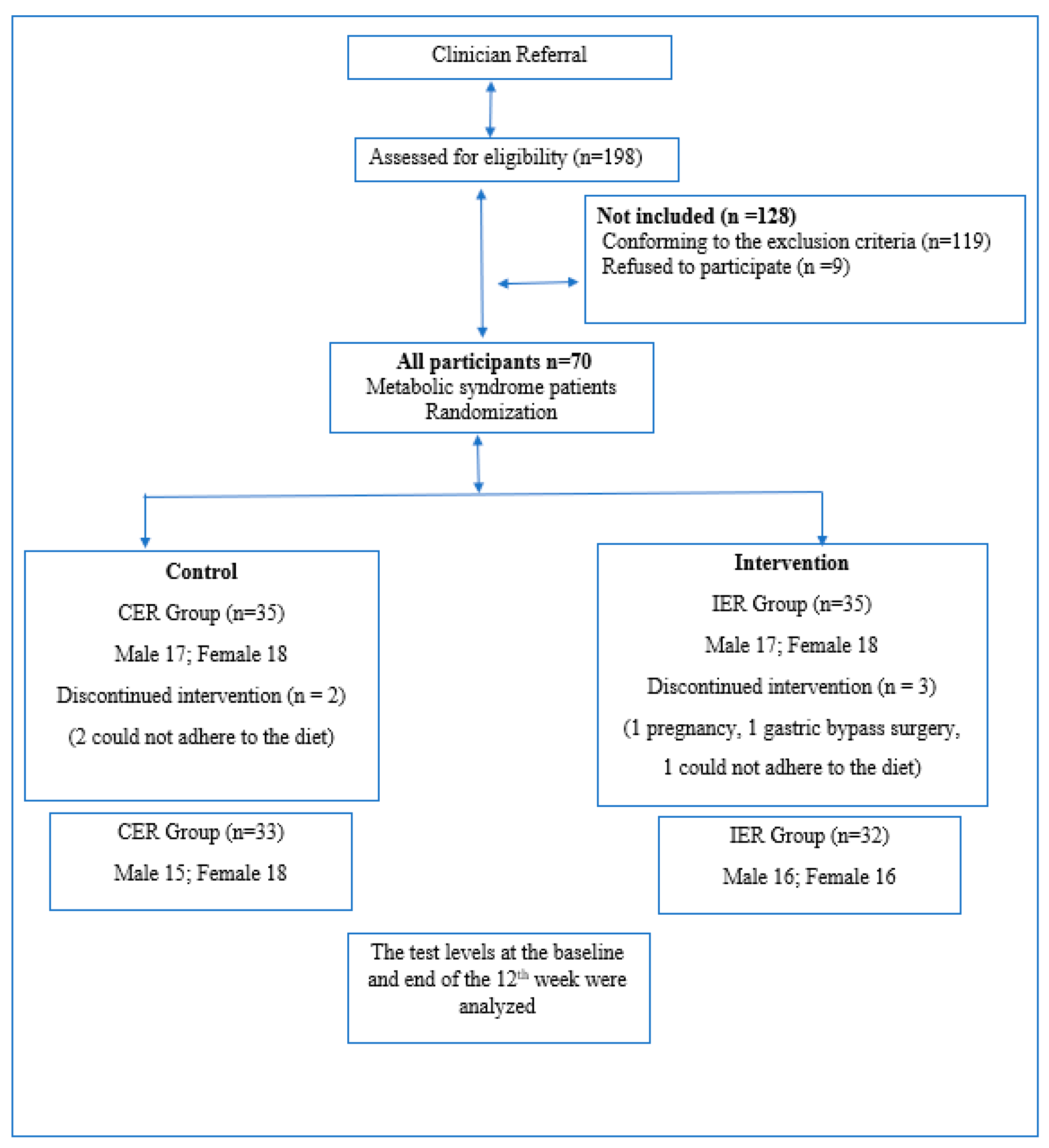







Post a Comment for "Intermittent Fasting And Alzheimer's Disease"