Paget's Disease Of Bone Histology
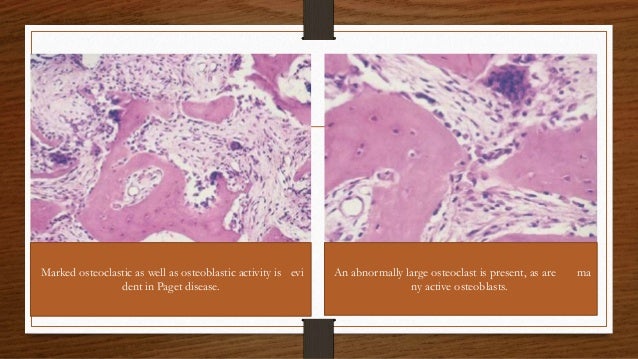
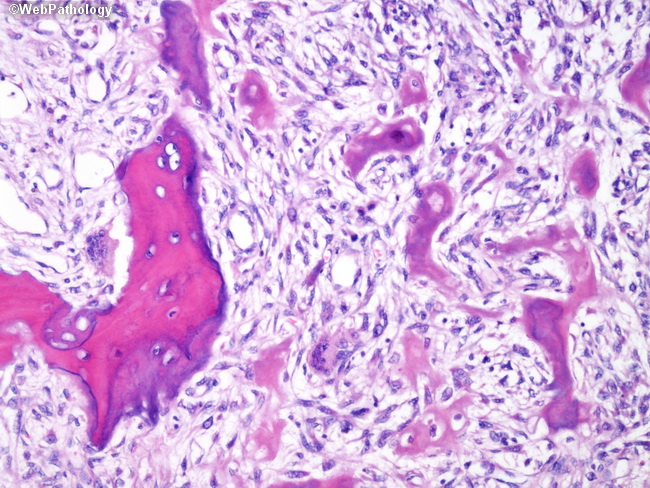
Paget's disease of bone histology. In this disease an initial rise in osteoclast activity is followed by a stage in which osteoclasts and osteoblasts are both active and finally by a stage in which osteoblasts dominate. The disorder is rarely recognized before age 40. Pagets disease is a progressive focal bone condition which can result in pain low quality of life deformity and other complications.
The histological hallmarks include the presence of. This can lead to distortion and compression of the posterior fossa and eventually internal hydrocephalus. It appears as an eczematous scaling pruritic eruption of the skin that clinically mimics inflammatory dermatoses.
Pagets Disease is a bone disorder characterized by unique histological findings. It was initially referred to as osteitis deformans as it was considered to be chronic inflammation of the bone. Invagination of base of skull due to weak bone compression of posterior fossa structures Associated neoplasms.
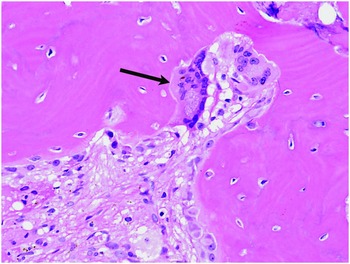
The result is an increase in bone mass but the bone is exaggerated. Osteoclast macrophage that reabsorbs bone matrix. Disease progression can be halted with potent bisphosphonates resulting in improvement in both quality of life and pain and normalisation of scintigraphy plain.
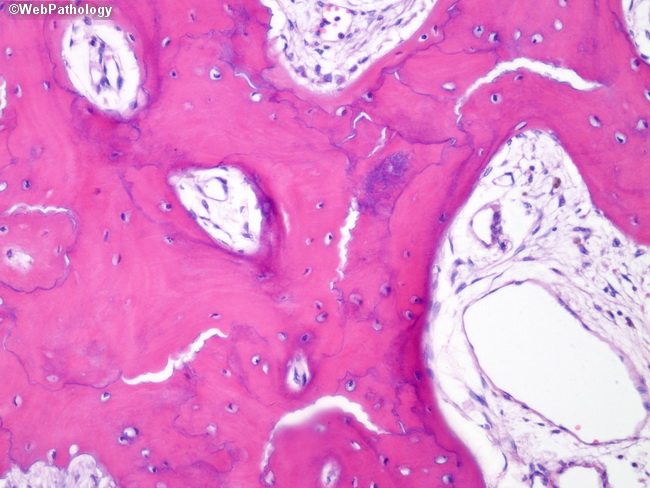
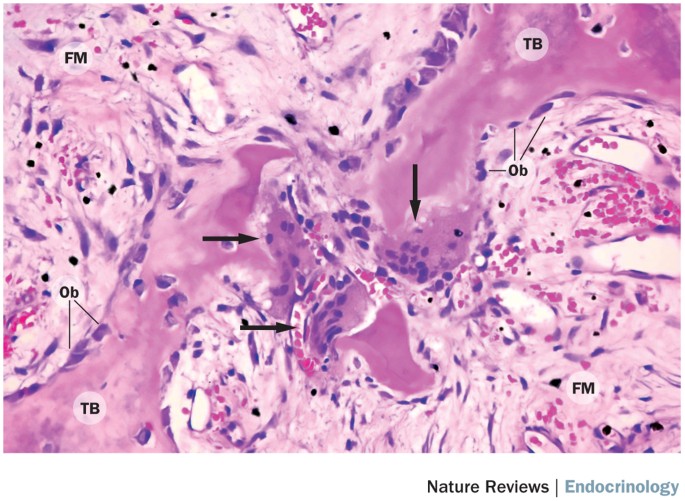
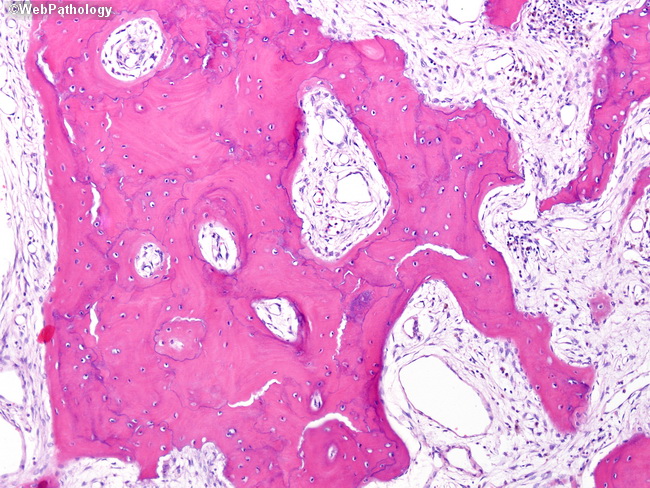
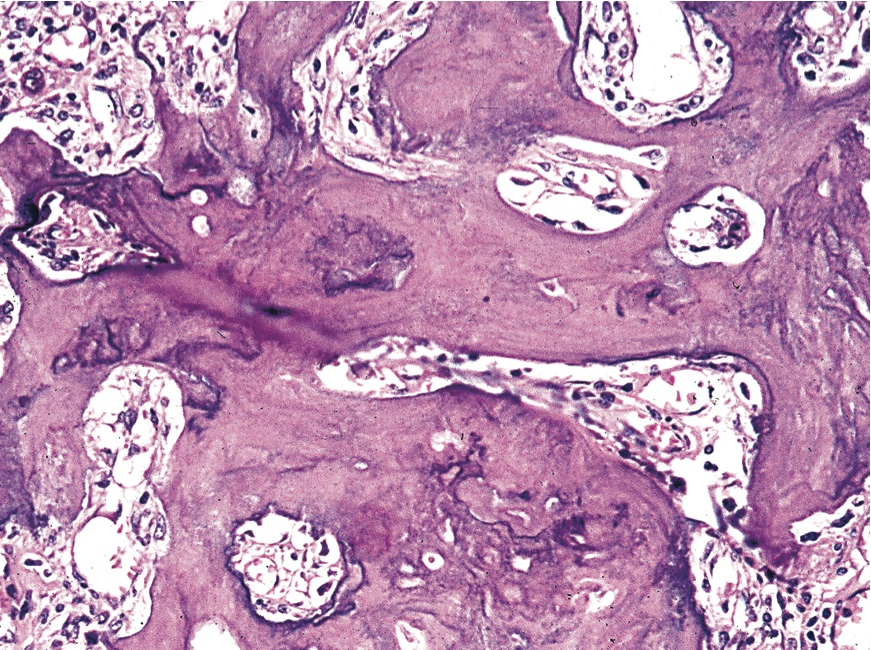
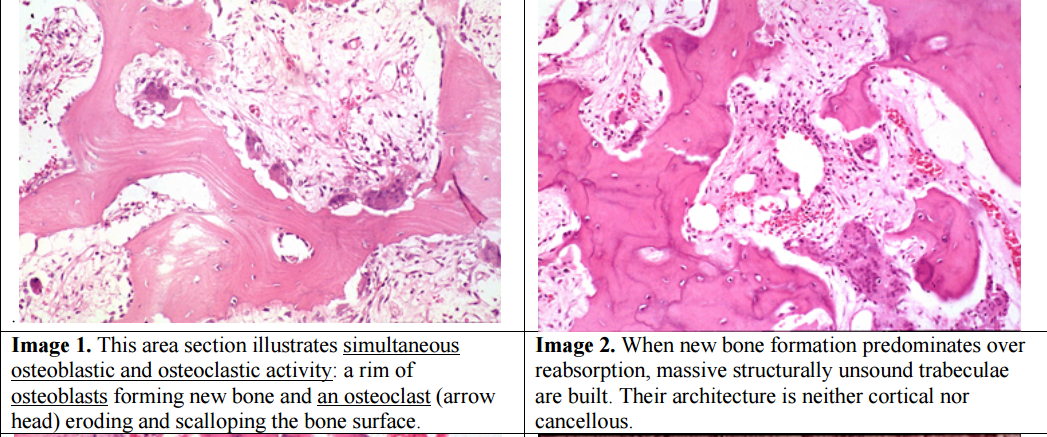
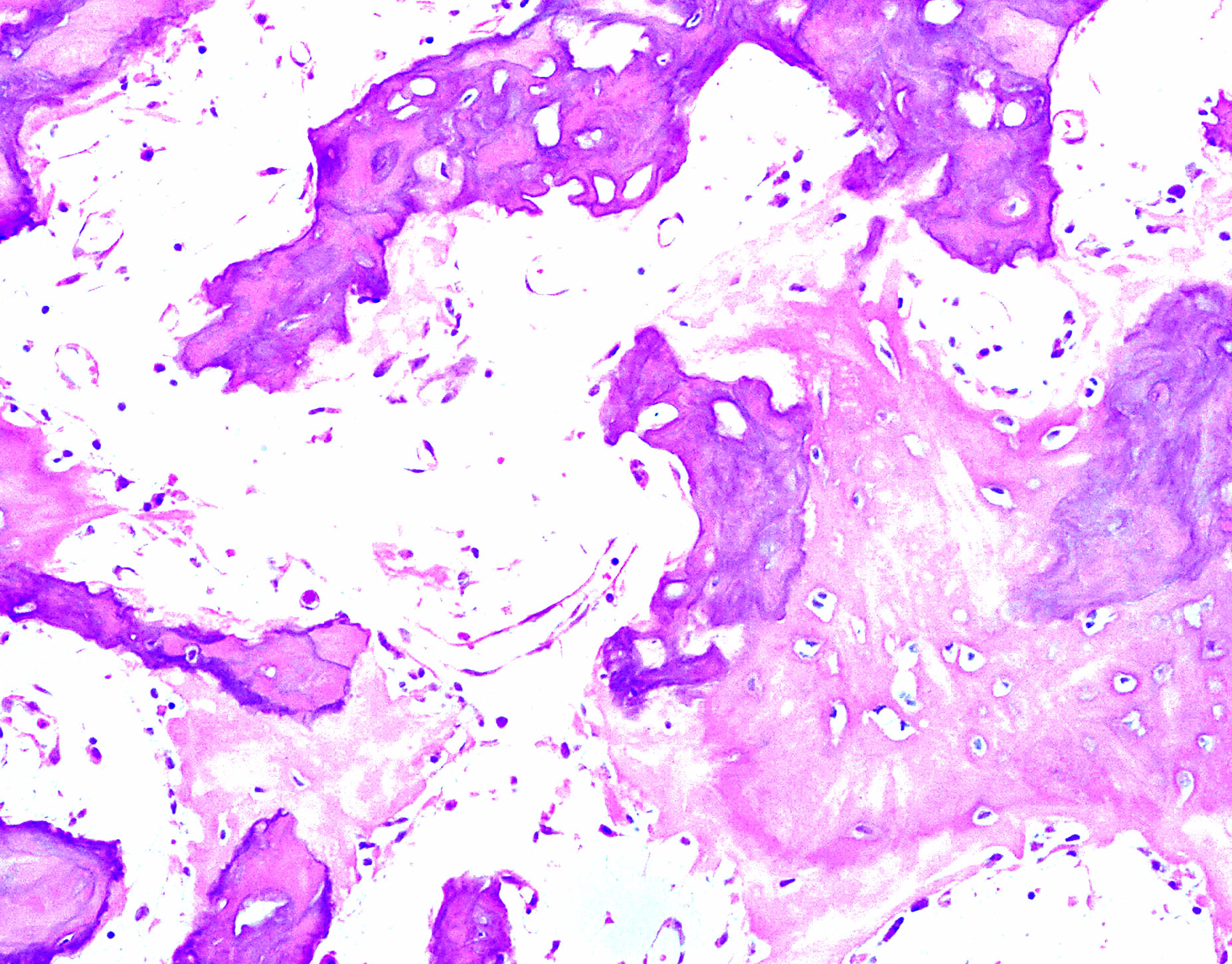
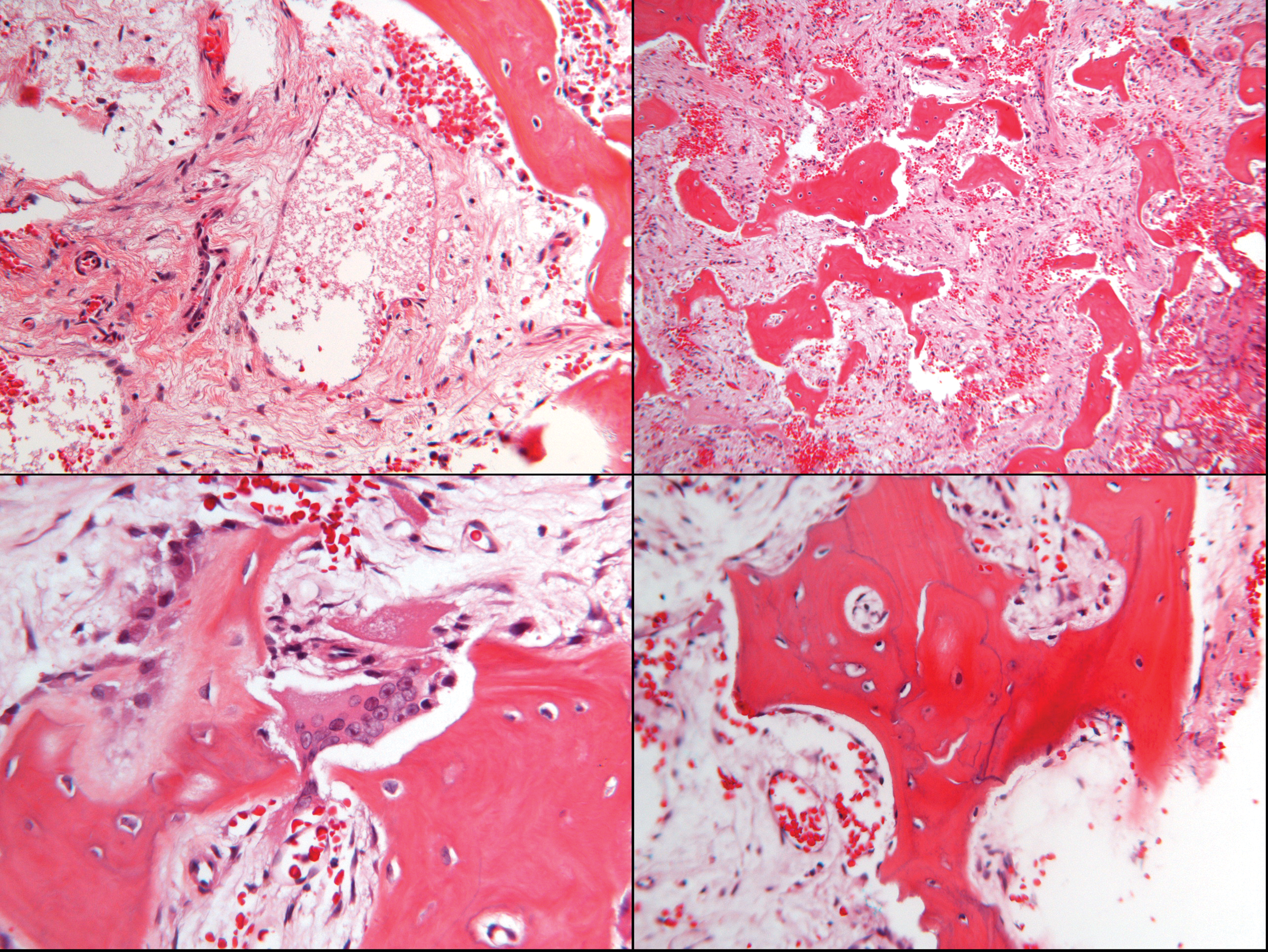
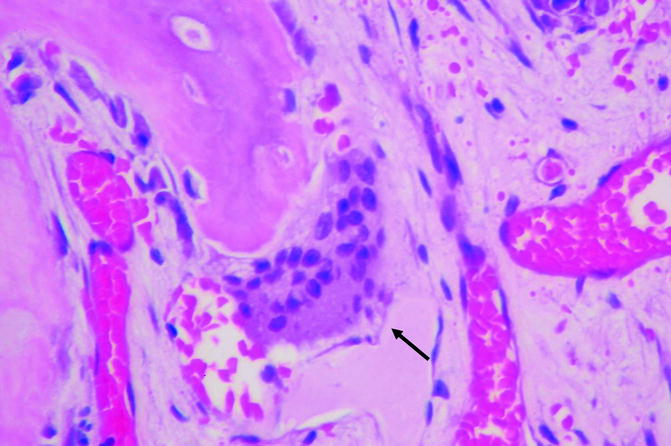
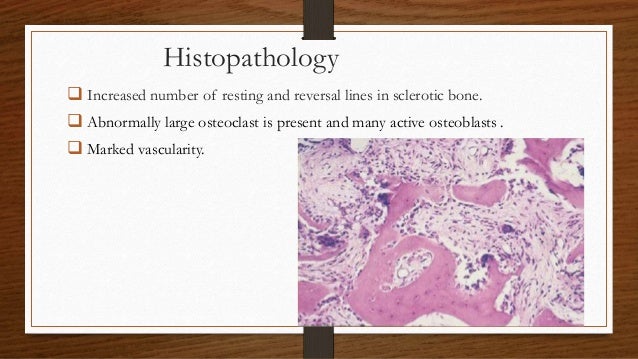
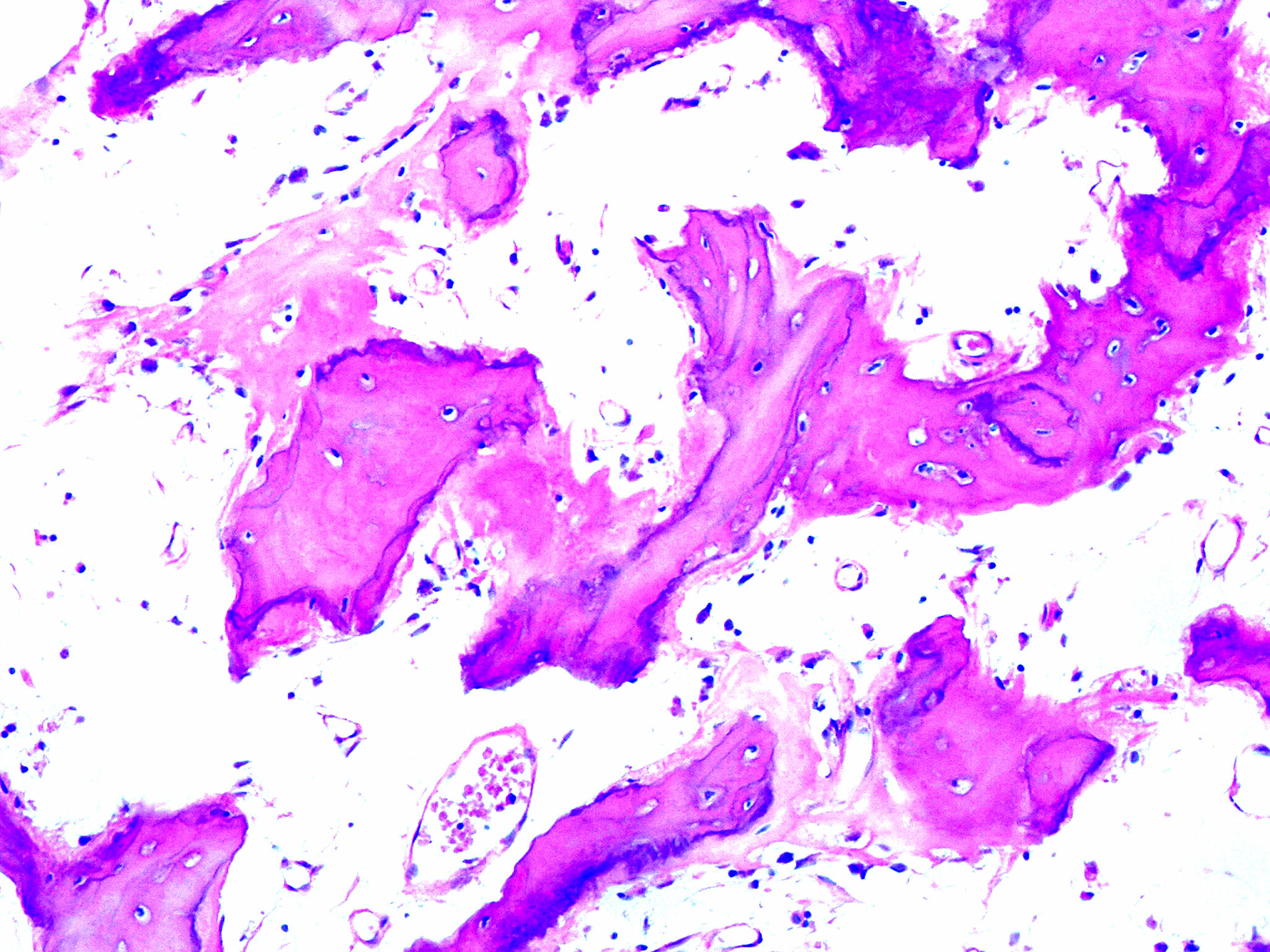
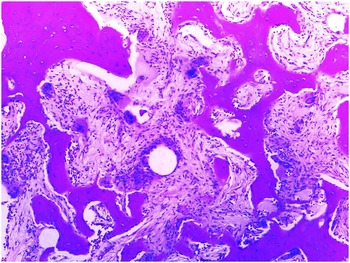
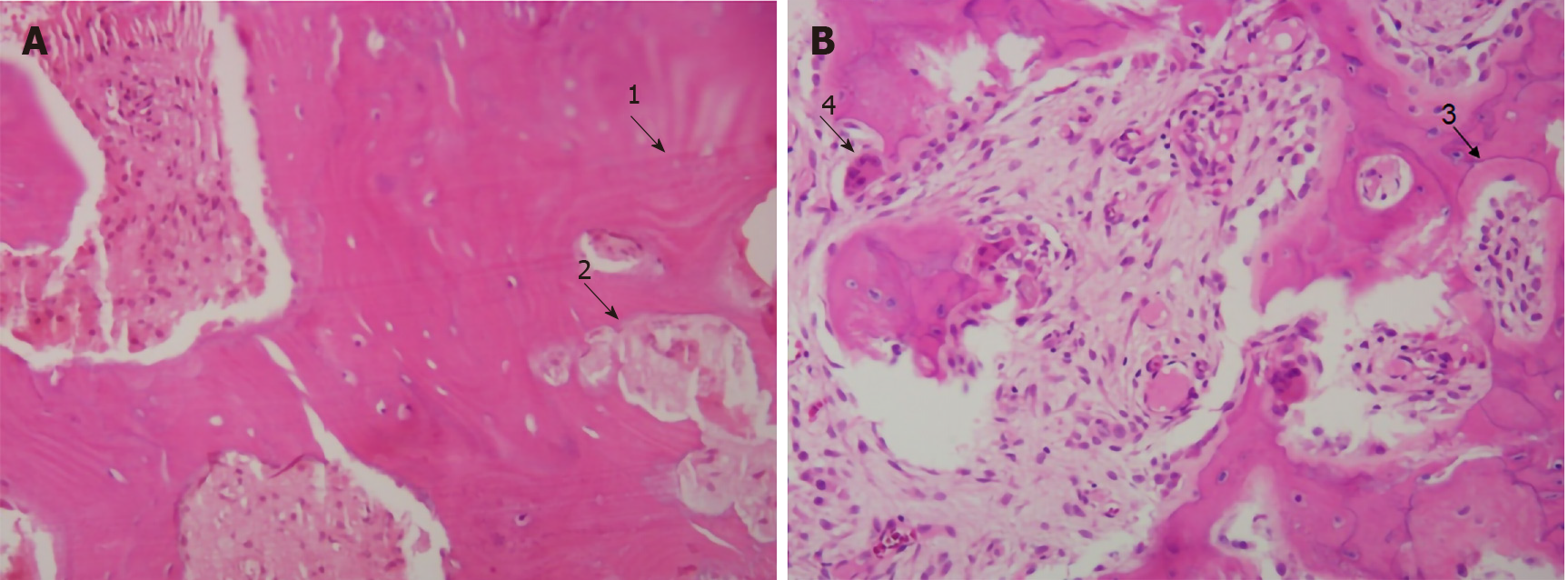
The bone is disorganized represented by the sloppy white marks in the bone and looks woven under polarized light. Usually associated with polyostotic Paget disease. 1 Today some 150 yr later it is well established that PDB is characterized by a localized excessive osteoclastic bone resorption that is followed by compensatory increased osteoblastic activity leading to unstructured fibroblastic and biomechanically unstable bone.
Pagets disease of bone is a common disease characterised by focal areas of increased bone turnover affecting one or several bones throughout the skeleton. Pagets disease of the base of the skull and the subsequent softening of the bone may lead to invagination by the cervical vertebrae. Sarcoma 5 with severe polyostotic disease giant cell tumor giant cell granuloma NOT related to Paget disease of breast or vulva although both discovered by Sir James Paget one of the founders of pathology.
P agets disease of bone PDB was first described by Sir James Paget in 1876. 2 The prevalence has been reported to be 10 to 15 by the ninth decade of life.
Pagets disease of the base of the skull and the subsequent softening of the bone may lead to invagination by the cervical vertebrae.
Disease progression can be halted with potent bisphosphonates resulting in improvement in both quality of life and pain and normalisation of scintigraphy plain. Histopathology Bone--Paget disease About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features 2021 Google LLC. Very poor prognosis with death due to pulmonary metastasis or local. Much older age than conventional osteosarcoma. Multicentric tumors associated with increasing localized pain. Pagets disease of bone is a common disease characterised by focal areas of increased bone turnover affecting one or several bones throughout the skeleton. Pagets disease is often asymptomatic but can be associated with bone pain and other complications such as osteoarthritis pathological fracture bone deformity deafness and nerve compression syndromes. The histological hallmarks include the presence of. It was described for the first time by Sir James Paget in 1877.
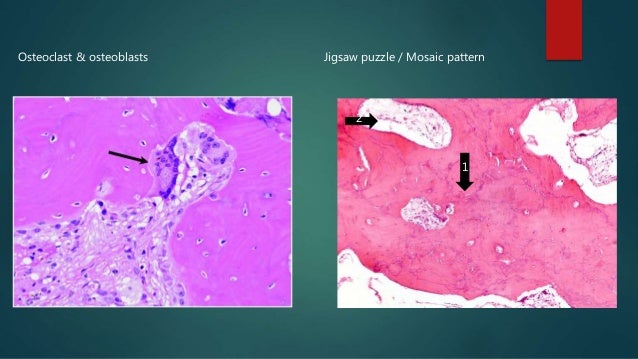
Pagets disease of bone PDB is a noninflammatory metabolic skeletal disorder characterized by localized excessive osteoclastic bone resorption that is followed by compensatory increased osteoblastic activity leading to unstructured fibroblastic and biomechanically unstable bone. Pagets disease is often asymptomatic but can be associated with bone pain and other complications such as osteoarthritis pathological fracture bone deformity deafness and nerve compression syndromes. Pagets disease of bone PDB is a noninflammatory metabolic skeletal disorder characterized by localized excessive osteoclastic bone resorption that is followed by compensatory increased osteoblastic activity leading to unstructured fibroblastic and biomechanically unstable bone. Pagets disease of the base of the skull and the subsequent softening of the bone may lead to invagination by the cervical vertebrae. 1 Today some 150 yr later it is well established that PDB is characterized by a localized excessive osteoclastic bone resorption that is followed by compensatory increased osteoblastic activity leading to unstructured fibroblastic and biomechanically unstable bone. Bone matrix has jigsaw-puzzle like pattern. In Pagets disease there is more bone volume average 42 of the area.




















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13569/histology-bone-tissue_english.jpg)



Post a Comment for "Paget's Disease Of Bone Histology"